Introduction
Edible oils are an essential part of cooking and nutrition across cultures and cuisines. From sizzling a stir-fry to adding depth to a salad dressing, these oils enhance flavor, texture, and provide key nutrients the body needs to function properly. Over centuries, the role of edible oils has evolved—not just as cooking staples but as key players in promoting health and wellness.
But what exactly are edible oils? Where do they come from, and how should we use them wisely? In this comprehensive guide, we explore everything you need to know about edible oils, including their types, uses, and how they can benefit your health.

What Is Edible Oil?
At its simplest, edible oil refers to any oil that is safe and suitable for human consumption. These oils are typically liquid at room temperature and are derived from plant, animal, or microbial sources.
Scientifically, edible oils are composed of lipids—mainly triglycerides—that serve as a dense source of energy. More than just calories, these oils are carriers of essential fatty acids, fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K), and antioxidants.
Sources of Edible Oil:
- Plant-Based Oils: Derived from seeds (like sunflower or canola), nuts (such as almonds and peanuts), or fruits (like olives and avocados).
- Animal-Based Oils: Such as fish oil, typically consumed as a supplement.
- Microbial Oils: Emerging oils produced by microorganisms, often used in specialty or vegan products.
The defining feature of edible oils is their safety for ingestion, in contrast to non-edible oils used for industrial or cosmetic purposes.
Types of Edible Oils
Edible oils come in a wide variety, each with its own flavor, nutrient profile, and ideal culinary application.The American Heart Association offers a helpful breakdown of cooking oils based on fat content, smoke point, and health implications.Here’s a breakdown of the most common types:
1. Seed-Based Oils
These oils are some of the most widely used due to their neutral flavor and high smoke points.
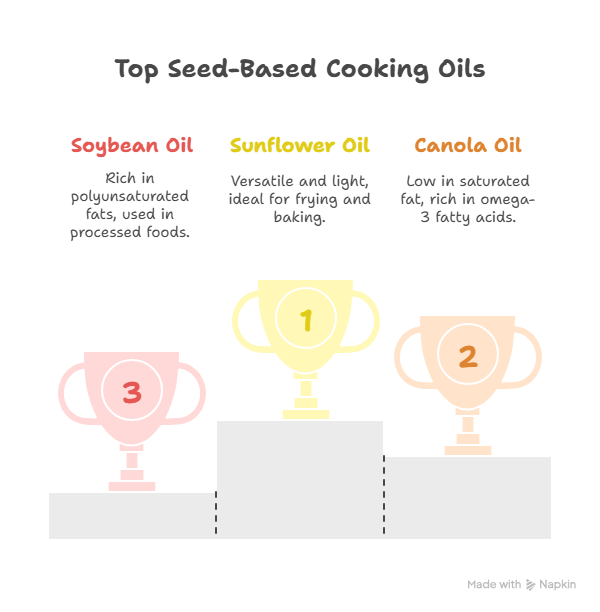
- Sunflower Oil: Light and versatile, good for frying and baking.
- Canola Oil: Low in saturated fat and high in omega-3 fatty acids.
- Soybean Oil: Rich in polyunsaturated fats; commonly used in processed foods.
- Safflower & Grapeseed Oils: Great for high-heat cooking with a mild taste.
2. Nut-Based Oils
Known for their rich, nutty flavors, these oils are often used in specialty dishes.
- Peanut Oil: Excellent for deep frying due to its high smoke point.
- Almond Oil: Used in both cooking and skin care; rich in vitamin E.
3. Fruit-Based Oils
Extracted from fruit flesh rather than seeds, these oils are prized for their flavor and health benefits.
- Olive Oil: Especially extra virgin olive oil (EVOO) is a cornerstone of the Mediterranean diet.
- Avocado Oil: High in monounsaturated fats; good for both cooking and raw uses.
- Coconut Oil: Contains medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs); popular in both cooking and skincare.
- Palm Oil: Widely used globally, though its sustainability is often debated.
4. Animal and Microbial Oils
While less common in everyday cooking, they’re nutritionally significant.
- Fish Oil: Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, often taken as a supplement for heart and brain health.
- Microbial Oils: Emerging as vegan alternatives, these are created through fermentation processes.
5. Refined vs. Cold-Pressed vs. Virgin Oils
- Refined Oils: Processed to remove impurities, extend shelf life, and withstand high heat.
- Cold-Pressed Oils: Extracted mechanically without heat, preserving nutrients and flavor.
- Virgin/Extra Virgin Oils: Typically cold-pressed with minimal processing; highest quality and nutrient-dense.
⚠️ Note: It’s helpful to contrast edible oils with non-edible oils (like motor oil or mineral oil) that are not fit for human use and may even be toxic if ingested.
Common Uses of Edible Oils
Edible oils are incredibly versatile, finding their way into kitchens and beauty routines alike. Here are the most popular uses:
1. Cooking
Edible oils are central to almost every cooking method:
- Frying & Sautéing: High-smoke-point oils like canola, sunflower, and peanut oil work best.
- Baking: Neutral oils like vegetable or grapeseed oil are often used in cakes and muffins.
- Roasting & Grilling: Olive and avocado oils add depth of flavor.
- Stir-Frying: Sesame oil brings aromatic flair to Asian dishes.
2. Salad Dressings & Marinades
Extra virgin olive oil, walnut oil, and flaxseed oil are favorites for cold applications, enhancing dishes without overpowering them.
3. Direct Consumption
Some oils are flavorful enough to be drizzled over dishes or served as dips. Olive oil and avocado oil are great examples.
4. Non-Culinary Uses
Several edible oils double as beauty products:
- Coconut & Almond Oil: Used in skincare and haircare for moisturizing and nourishment.
- Castor Oil: Traditionally used for hair growth and digestion (in small, controlled amounts).
Health Benefits of Edible Oils
Beyond flavor and function, edible oils can significantly impact your health. Choosing the right oils and using them in moderation is key to gaining their benefits without overconsumption.According to experts at Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, replacing saturated fats with healthier unsaturated fats can reduce the risk of heart disease.
1. Essential Fatty Acids
Edible oils are primary sources of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, which support:
- Brain development and function
- Hormone production
- Inflammation regulation
2. Heart Health
Monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats found in oils like olive, avocado, and canola are linked to:
- Lower LDL (bad) cholesterol
- Reduced risk of cardiovascular disease
- Improved blood pressure levels
3. Vitamin E and Antioxidants
Oils like sunflower, almond, and wheat germ oil are rich in vitamin E, a potent antioxidant that supports skin health and immune function.
4. Metabolic & Hormonal Function
Dietary fats play a crucial role in:
- Absorbing fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K)
- Supporting thyroid and reproductive hormones
- Maintaining cellular structure and metabolism
5. Saturated vs. Unsaturated vs. Trans Fats
- Unsaturated Fats (Good): Found in olive, avocado, and flaxseed oil; promote heart and brain health.
- Saturated Fats (Use Sparingly): Present in coconut and palm oil; should be consumed in moderation.
- Trans Fats (Avoid): Often found in hydrogenated oils; linked to heart disease and inflammation.
✅ Pro Tip: Choose cold-pressed, unrefined oils when possible—they retain more antioxidants and nutrients compared to heavily processed oils.
Choosing the Right Edible Oil
Not all oils are created equal. Here’s how to select the best oil for your needs:
1. Smoke Point
The smoke point is the temperature at which oil starts to burn and produce smoke. Using oil past this point can degrade flavor and release harmful compounds.
- High Smoke Point (Best for frying): Avocado oil, peanut oil, canola oil
- Low Smoke Point (Best for dressings): Extra virgin olive oil, flaxseed oil
2. Flavor Profile
- Neutral Oils: Canola, grapeseed—ideal for everyday cooking.
- Strong-Flavored Oils: Sesame, walnut, or EVOO—great for flavoring.
3. Nutritional Quality
Always check labels for:
- Fat composition (more unsaturated = better)
- Processing method (cold-pressed vs. refined)
- Added preservatives or artificial flavors
4. Storage Tips
To maintain freshness and quality:
- Store oils in a cool, dark place
- Keep containers tightly sealed
- Watch for signs of rancidity—off smells or flavors indicate spoilage
Conclusion
Edible oils are more than just cooking ingredients—they’re nutritional powerhouses that can support heart health, brain function, and overall wellness. From the delicate taste of extra virgin olive oil to the high-heat resilience of avocado oil, each type serves a purpose in your kitchen and your diet.
By understanding the types of oils available, their uses, and health implications, you can make smarter choices that benefit both your meals and your long-term health.”For a more detailed, science‑backed breakdown of which cooking oils suit different health goals and cooking methods, check out ‘The Best Oil for Your Diet: A Science‑Backed Guide to Healthy Cooking Oils’ by Edible Oil Expert.”
So next time you’re in the oil aisle, don’t just reach for the familiar—choose the oil that best fits your cooking method, taste preference, and nutritional goals
